Question 1. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin.
Answer. (d) Cytokinin
Question 2. The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) dendrite.
(b) synapse.
(c) axon.
(d) impulse.
Answer. (b) synapse
Question 3. The brain is responsible for
(a) thinking.
(b) regulating the heart beat.
(c) balancing the body.
(d) all of the above.
Answer. (d) all of the above.
Question 4. What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer. The main function of receptors in our body is to detect information from our environment. These receptors are usually located in our sense organs, such as the inner ear, the nose, the tongue, skin etc. The information is transferred to brain through an organised network of nerve cells for processing. A synapse links Axon of neuron with dendrite of other neuron in chain and carry out neural communication through series of electrical impulses and chemical reactions
There may be situations, where receptors do not work properly. For example, gustatory receptors in tongue detect taste while olfactory receptors in nasal cavity detect smell. In case, if they do not work properly, the food will have no taste or may taste differently. Also, in the absence of smell, we may end up eating spoiled food or rotten fruits
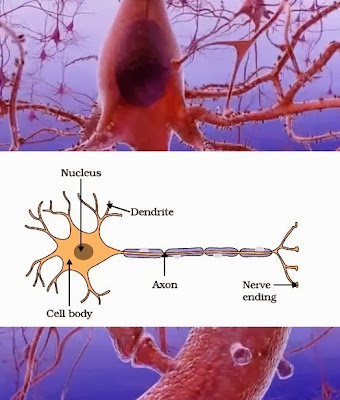
Question 5. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Answer. Function of a neuron : The neuron, at functional level, is a elementary part of our nervous system. It consists of three main parts : (i) Dendrites - where information is acquired
(ii)Cell body - through which information travels as an electrical impulse
(iii)Axon where this impulse must be converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission.
This information, acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals.
These chemicals cross the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. In this way information is exchanged in the form of electrical impulses from one part of the body to another through an organised network of nerves passing through spinal cord and connecting brain with others.
Question 6. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer. Plants show tropism in response to different environmental triggers such as light. The directional, or tropic, movement towards the light or away from it is called phototropism. In phototropism, shoots respond by bending towards light while roots respond by bending away from it.
Question 7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer. (i) All the signals and responses with in nervous system, which are exchanged between brain and different body parts through spinal cord may get disturbed causing impaired functioning of different body parts like in paralysis
(ii) Reflex actions which are controlled by spinal arcs without the help of brain may also get impaired
Question 8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer.In plants, stimulated cells release a chemical compound, know as plant hormones. These plant hormones used by multicellular organisms for control and coordination show a great deal of diversity. Different plant hormones help to coordinate growth, development and responses to the environment. They are synthesised and processed at places away from where they act and simply diffuse to the area of action.
Question 9. What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Answer. In the living organisms, every change in the environment around evokes an appropriate movement in response by them. For example - falling of a bright light on eyes, touching of hot surface, exposure to cold weather evokes different reactions. When we want to talk to our friends in class, we whisper, rather than shouting loudly. And when in danger, we cry or shout. Hence, the movement to be made depends on the event that is triggering it. Therefore, such controlled movement must be connected to the recognition of various events in the environment, followed by only the correct movement in response. In other words, living organisms must use systems providing control and coordination. In keeping with the general principles of body organisation in multicellular organisms, specialised tissues are used to provide these control and coordination activities.
Question 10. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Answer. Involuntary actions : These are muscle movements over which we do not have any thinking control. For example : heart beating, salivation and vomiting. Many of these involuntary actions are controlled by the mid-brain and hind-brain
Reflex actions : A reflex action in living bodies, is an efficient ways of functioning in response to some situation without any thought processes under taken by brain.The thinking process of the brain is not fast enough to react against all situations. Reflex actions are controlled by the spinal arcs present with in spinal cord without the help of brain. Examples : closing of eyes as bright light falls on them, fingers moving away on touching of hot surface, sneezing
Question 11. Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Answer. In human beings, the nervous system controls the various functions by well organised network of neurons. All information from our environment is detected by the receptors present in our sensory organs and transferred to brain and other parts through neural network in the form of series of electrical impulses and chemical changes.
Apart from this certain important function like maintaining blood sugar level, metabolism, feeling of joy , feeling of sorrow and anger, demand of extra strength to meet a specific situation by the living body, development and growth of body etc all are controlled by the diverse types of hormones secreted by various endocrine glands. In fact nervous and hormonal mechanisms together perform the function of maintaining control and coordination in animals
Question 12. What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Answer. Movement in sensitive plant : Movement in sensitive plant takes place in leaves in response to touch. On touching, a stimulus is conducted to its base which triggers a decrease in osmotic pressure causing leaves to shrink. Leaves retain their position once the stimulus is over. This is a growth independent movement. This movement happens at a point different from the point of touch. So, information that a touch has occurred must be communicated. The plants also use electrical-chemical means to convey this information from cell to cell, but unlike in animals, there is no specialised tissue in plants for the conduction of information. Finally, again as in animals, some cells must change shape in order for movement to happen. Instead of the specialised proteins found in animal muscle cells, plant cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them, resulting in swelling or shrinking, and therefore in changing shapes.
Movement in our leg : Movement in our legs are controlled by the nerves which are connected to muscles. The nerve gets the control signal from brains in the form of electrical impulses. On reaching at leg muscles, the impulse is converted into a chemical signal and the muscles contract to lift the leg. Movement of legs takes place due to muscle contraction and subsequent relaxation, which is controlled by our nervous system. In nervous system Electrical impulses are an excellent means for fast information transfer. But there are limitations to the use of electrical impulses. Firstly, they will reach only those cells that are connected by nervous tissue, not each and every cell in the animal body. Secondly, cells cannot continually create and transmit electrical impulses as it takes some time to reset its mechanisms before it can generate and transmit a new impulse. To overcome this, most multicellular organisms use another means of communication between cells, namely, chemical communication with hormones as messengers. Hormones get diffuse all around the original cell.Special molecules on presents on the surfaces of surrounding cells, are able to recognise information from the hormonal chemicals, and even transmit it. This is a bit slow process, but it can potentially reach all cells of the body (for example through blood in humans) regardless of nervous connections, and it can be done steadily and persistently
===========================================
Activity 7.1 | Page 115 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Question 1. Put some sugar in your mouth. How does it taste?
Answer. The taste is sweet and is a combined perception of our sensory organs tongue and nose.
Question 2. Block your nose by pressing it between your thumb and index finger. Now eat sugar again. Is there any difference in its taste?
Answer. Yes,there is noticeable difference in its taste. As stated above, the general perception of taste, which we have for any particular eatable substance, is jointly created by our sense organs tongue and nose through receptors. Gustatory receptors in tongue will detect taste while olfactory receptors in nasal cavity will detect smell. This is due to the reason, when we have cold, the taste of things changes due to blocked nose
Question 3. While eating lunch, block your nose in the same way and notice if you can fully appreciate the taste of the food you are eating.
Answer. Students can try themselves. Due to non functioning of olfactory receptors present in nose, the Salivary Amylase secreted by salivary glands, which makes our food juicy and tasty, may not be there. As a result, there will be difference in taste, we can not fully appreciate the taste of the food we are eating
Intext Questions | Page 119 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Question 1. What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer. A reflex action in living bodies, is an efficient ways of functioning in response to some situation without any thought processes under taken by brain.The thinking process of the brain is not fast enough to react against all situations. Reflex actions are controlled by the spinal arcs present with in spinal cord without the help of brain.
Where as, walking is well thought of action by the brain, which involves planned and controlled performance of different body parts.
Question 2. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer. Synapse is the region of joining between dendrite and axon of two neurons, which plays an important role in in the exchange of the information in nervous system. The information, acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals in the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. This is how nervous impulses travel in the body.
Question 3. Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer. Cerebellum which is part of the hind-brain, is responsible for precision of voluntary actions and maintaining the posture and equilibrium of the body.
Question 4. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Answer. The smell of an agarbatti is detected through olfactory receptors by our fore-brain which is the main thinking part of our brain. It has regions which receive sensory impulses from various receptors. Separate areas of the fore-brain are specialised for hearing, smell, sight and so on. There are separate areas of association where this sensory information is interpreted by putting it together with information from other receptors as well as with information that is already stored in the brain.
Question 5. What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer. There is no active role of brain in reflex action. Nerves from all over the body meet in a bundle in the spinal cord on their way to the brain. The Reflex arcs which are formed in spinal cord itself where nerves first meet each other, are solely responsible for all reflex action, although the information is also supplied to the brain for future reference
Activity 7.2 | Page 121 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Answer. In case of the old parts of the shoot and root, change in direction is less and not much noticeable , however there is marked and noticeable change in case of new parts of the shoot and root
Question 2. Are there differences in the direction of the new growth?
Answer. Yes, new growth of parts of the shoot and root is visibly more noticeable. Shoots are found bending towards light while roots are found bending away from it
Question 3. What can we conclude from this activity?
Answer. As Shoots are found bending towards light while roots are found bending away from it, we can conclude from this activity that shoots show phototropism and the roots show geotropism.
Intext Questions | Page 122 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Question 1. What are plant hormones?
Answer. Plant hormones are the chemical compounds released by the stimulated cells of a plant. They are responsible for the chemical communication between cells, which ultimately help plant to coordinate its growth, development , various activities and responses to the environment
Question 2. How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer. The movement of leaves of the sensitive plant are different from the movement of a shoot towards light. The leaves of the sensitive plant move very quickly in response to touch.There is no growth involved in this movement and is not directional. Where as the movement of a shoot towards light is caused by growth and is directional.
Question 3. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer. (i) In growing plants, light detection results in synthesis of a plant hormone called Auxin, at the shoot tip and helps the cells to grow longer. Opposite from the light side, auxin diffuses more towards the shady side of the shoot and stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light. Thus, the plant appears to bend or grow towards light.
(ii) Similarly, gibberellins are another example of plant hormones which, like auxins, help in the growth of the stem.
Question 4. How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer. Some plants like the pea plant, to support theirs growth make use of tendrils to climb upon other plants or supports. These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, the plant hormone auxin diffuses more towards the unsupported side of the tendrils and stimulates the cells to grow rapidly than the other supported side which is in contact. This difference in the growth of surface cells results in curling of tendrils around the support and help in plant growth and its clinging to the support
Question 5. Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer. Plants show tropism in response to different stimuli. Hydrotropism is directional growth movements in plants caused by water. Positive hydrotropism can be demonstrated with germinated seedings, which are allowed to grow on ground. The soil under the roots is separated by a polythene partition. The left side is kept moist but the right side is kept dry. The radicals at first grow in downward direction due to the effect of gravity (positive geotropism) and light (Negative phototropism), but after some time, the roots bend toward the moist soil (Positive hydrotropism). This is evidently due to the affinity of germinating roots towards water.
Activity 7.3 | Page 123 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Answer. The endocrine glands are :
Intext Questions | Page 125 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Question 1. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer. Chemical coordination takes place in animals through endocrine system which constitutes a second way of control and coordination in our body. Different endocrine glands, secret chemical substances called hormones to control and coordinate different body activities. It is important that hormones should be secreted in precise quantities. The timing and amount of hormone released are regulated by feedback mechanisms
Question 2. Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer. The use of iodised salt advisable because Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make thyroxin hormone. Thyroxin regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth. Iodine is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin. In case iodine is deficient in our diet, there is a possibility that we might suffer from goitre. One of the symptoms in this disease is a swollen neck.
Question 3. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Answer. When Adrenaline is secreted into the blood and carried to different parts of the body. The target organs such as heart, beats faster, resulting in increased supply of oxygen to our muscles which as a result, get surplus power to perform various activities against different demanding situations
Question 4. Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer.The patients of diabetes, who have inadequate levels of insulin produced by pancreas, are treated by giving injections of insulin. Insulin is a hormone which is produced by the pancreas and helps in regulating blood sugar levels. If it is not secreted in proper amounts, the sugar level in the blood rises causing many harmful effects.
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin.
Answer. (d) Cytokinin
Question 2. The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) dendrite.
(b) synapse.
(c) axon.
(d) impulse.
Answer. (b) synapse
Question 3. The brain is responsible for
(a) thinking.
(b) regulating the heart beat.
(c) balancing the body.
(d) all of the above.
Answer. (d) all of the above.
Question 4. What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer. The main function of receptors in our body is to detect information from our environment. These receptors are usually located in our sense organs, such as the inner ear, the nose, the tongue, skin etc. The information is transferred to brain through an organised network of nerve cells for processing. A synapse links Axon of neuron with dendrite of other neuron in chain and carry out neural communication through series of electrical impulses and chemical reactions
There may be situations, where receptors do not work properly. For example, gustatory receptors in tongue detect taste while olfactory receptors in nasal cavity detect smell. In case, if they do not work properly, the food will have no taste or may taste differently. Also, in the absence of smell, we may end up eating spoiled food or rotten fruits
Question 5. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Answer. Function of a neuron : The neuron, at functional level, is a elementary part of our nervous system. It consists of three main parts : (i) Dendrites - where information is acquired
(ii)Cell body - through which information travels as an electrical impulse
(iii)Axon where this impulse must be converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission.
This information, acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals.
These chemicals cross the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. In this way information is exchanged in the form of electrical impulses from one part of the body to another through an organised network of nerves passing through spinal cord and connecting brain with others.
Question 6. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer. Plants show tropism in response to different environmental triggers such as light. The directional, or tropic, movement towards the light or away from it is called phototropism. In phototropism, shoots respond by bending towards light while roots respond by bending away from it.
Question 7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer. (i) All the signals and responses with in nervous system, which are exchanged between brain and different body parts through spinal cord may get disturbed causing impaired functioning of different body parts like in paralysis
(ii) Reflex actions which are controlled by spinal arcs without the help of brain may also get impaired
Question 8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer.In plants, stimulated cells release a chemical compound, know as plant hormones. These plant hormones used by multicellular organisms for control and coordination show a great deal of diversity. Different plant hormones help to coordinate growth, development and responses to the environment. They are synthesised and processed at places away from where they act and simply diffuse to the area of action.
Question 9. What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Answer. In the living organisms, every change in the environment around evokes an appropriate movement in response by them. For example - falling of a bright light on eyes, touching of hot surface, exposure to cold weather evokes different reactions. When we want to talk to our friends in class, we whisper, rather than shouting loudly. And when in danger, we cry or shout. Hence, the movement to be made depends on the event that is triggering it. Therefore, such controlled movement must be connected to the recognition of various events in the environment, followed by only the correct movement in response. In other words, living organisms must use systems providing control and coordination. In keeping with the general principles of body organisation in multicellular organisms, specialised tissues are used to provide these control and coordination activities.
Question 10. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Answer. Involuntary actions : These are muscle movements over which we do not have any thinking control. For example : heart beating, salivation and vomiting. Many of these involuntary actions are controlled by the mid-brain and hind-brain
Reflex actions : A reflex action in living bodies, is an efficient ways of functioning in response to some situation without any thought processes under taken by brain.The thinking process of the brain is not fast enough to react against all situations. Reflex actions are controlled by the spinal arcs present with in spinal cord without the help of brain. Examples : closing of eyes as bright light falls on them, fingers moving away on touching of hot surface, sneezing
Question 11. Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Answer. In human beings, the nervous system controls the various functions by well organised network of neurons. All information from our environment is detected by the receptors present in our sensory organs and transferred to brain and other parts through neural network in the form of series of electrical impulses and chemical changes.
Apart from this certain important function like maintaining blood sugar level, metabolism, feeling of joy , feeling of sorrow and anger, demand of extra strength to meet a specific situation by the living body, development and growth of body etc all are controlled by the diverse types of hormones secreted by various endocrine glands. In fact nervous and hormonal mechanisms together perform the function of maintaining control and coordination in animals
Question 12. What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Answer. Movement in sensitive plant : Movement in sensitive plant takes place in leaves in response to touch. On touching, a stimulus is conducted to its base which triggers a decrease in osmotic pressure causing leaves to shrink. Leaves retain their position once the stimulus is over. This is a growth independent movement. This movement happens at a point different from the point of touch. So, information that a touch has occurred must be communicated. The plants also use electrical-chemical means to convey this information from cell to cell, but unlike in animals, there is no specialised tissue in plants for the conduction of information. Finally, again as in animals, some cells must change shape in order for movement to happen. Instead of the specialised proteins found in animal muscle cells, plant cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them, resulting in swelling or shrinking, and therefore in changing shapes.
Movement in our leg : Movement in our legs are controlled by the nerves which are connected to muscles. The nerve gets the control signal from brains in the form of electrical impulses. On reaching at leg muscles, the impulse is converted into a chemical signal and the muscles contract to lift the leg. Movement of legs takes place due to muscle contraction and subsequent relaxation, which is controlled by our nervous system. In nervous system Electrical impulses are an excellent means for fast information transfer. But there are limitations to the use of electrical impulses. Firstly, they will reach only those cells that are connected by nervous tissue, not each and every cell in the animal body. Secondly, cells cannot continually create and transmit electrical impulses as it takes some time to reset its mechanisms before it can generate and transmit a new impulse. To overcome this, most multicellular organisms use another means of communication between cells, namely, chemical communication with hormones as messengers. Hormones get diffuse all around the original cell.Special molecules on presents on the surfaces of surrounding cells, are able to recognise information from the hormonal chemicals, and even transmit it. This is a bit slow process, but it can potentially reach all cells of the body (for example through blood in humans) regardless of nervous connections, and it can be done steadily and persistently
===========================================
Activity 7.1 | Page 115 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Question 1. Put some sugar in your mouth. How does it taste?
Answer. The taste is sweet and is a combined perception of our sensory organs tongue and nose.
Question 2. Block your nose by pressing it between your thumb and index finger. Now eat sugar again. Is there any difference in its taste?
Answer. Yes,there is noticeable difference in its taste. As stated above, the general perception of taste, which we have for any particular eatable substance, is jointly created by our sense organs tongue and nose through receptors. Gustatory receptors in tongue will detect taste while olfactory receptors in nasal cavity will detect smell. This is due to the reason, when we have cold, the taste of things changes due to blocked nose
Question 3. While eating lunch, block your nose in the same way and notice if you can fully appreciate the taste of the food you are eating.
Answer. Students can try themselves. Due to non functioning of olfactory receptors present in nose, the Salivary Amylase secreted by salivary glands, which makes our food juicy and tasty, may not be there. As a result, there will be difference in taste, we can not fully appreciate the taste of the food we are eating
Intext Questions | Page 119 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Question 1. What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer. A reflex action in living bodies, is an efficient ways of functioning in response to some situation without any thought processes under taken by brain.The thinking process of the brain is not fast enough to react against all situations. Reflex actions are controlled by the spinal arcs present with in spinal cord without the help of brain.
Where as, walking is well thought of action by the brain, which involves planned and controlled performance of different body parts.
Question 2. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer. Synapse is the region of joining between dendrite and axon of two neurons, which plays an important role in in the exchange of the information in nervous system. The information, acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals in the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. This is how nervous impulses travel in the body.
Question 3. Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer. Cerebellum which is part of the hind-brain, is responsible for precision of voluntary actions and maintaining the posture and equilibrium of the body.
Question 4. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Answer. The smell of an agarbatti is detected through olfactory receptors by our fore-brain which is the main thinking part of our brain. It has regions which receive sensory impulses from various receptors. Separate areas of the fore-brain are specialised for hearing, smell, sight and so on. There are separate areas of association where this sensory information is interpreted by putting it together with information from other receptors as well as with information that is already stored in the brain.
Question 5. What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer. There is no active role of brain in reflex action. Nerves from all over the body meet in a bundle in the spinal cord on their way to the brain. The Reflex arcs which are formed in spinal cord itself where nerves first meet each other, are solely responsible for all reflex action, although the information is also supplied to the brain for future reference
Activity 7.2 | Page 121 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
- Fill a conical flask with water.
- Cover the neck of the flask with a wire mesh.
- Keep two or three freshly germinated bean seeds on the wire mesh.
- Take a cardboard box which is open from one side.
- Keep the flask in the box in such a manner that the open side of the box faces light coming from a window
- After two or three days, you will notice that the shoots bend towards light and roots away from light.
- Now turn the flask so that the shoots are away from light and the roots towards light. Leave it undisturbed in this condition for a few days.
Answer. In case of the old parts of the shoot and root, change in direction is less and not much noticeable , however there is marked and noticeable change in case of new parts of the shoot and root
Question 2. Are there differences in the direction of the new growth?
Answer. Yes, new growth of parts of the shoot and root is visibly more noticeable. Shoots are found bending towards light while roots are found bending away from it
Question 3. What can we conclude from this activity?
Answer. As Shoots are found bending towards light while roots are found bending away from it, we can conclude from this activity that shoots show phototropism and the roots show geotropism.
Intext Questions | Page 122 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Question 1. What are plant hormones?
Answer. Plant hormones are the chemical compounds released by the stimulated cells of a plant. They are responsible for the chemical communication between cells, which ultimately help plant to coordinate its growth, development , various activities and responses to the environment
Question 2. How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer. The movement of leaves of the sensitive plant are different from the movement of a shoot towards light. The leaves of the sensitive plant move very quickly in response to touch.There is no growth involved in this movement and is not directional. Where as the movement of a shoot towards light is caused by growth and is directional.
Question 3. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer. (i) In growing plants, light detection results in synthesis of a plant hormone called Auxin, at the shoot tip and helps the cells to grow longer. Opposite from the light side, auxin diffuses more towards the shady side of the shoot and stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light. Thus, the plant appears to bend or grow towards light.
(ii) Similarly, gibberellins are another example of plant hormones which, like auxins, help in the growth of the stem.
Question 4. How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer. Some plants like the pea plant, to support theirs growth make use of tendrils to climb upon other plants or supports. These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, the plant hormone auxin diffuses more towards the unsupported side of the tendrils and stimulates the cells to grow rapidly than the other supported side which is in contact. This difference in the growth of surface cells results in curling of tendrils around the support and help in plant growth and its clinging to the support
Question 5. Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer. Plants show tropism in response to different stimuli. Hydrotropism is directional growth movements in plants caused by water. Positive hydrotropism can be demonstrated with germinated seedings, which are allowed to grow on ground. The soil under the roots is separated by a polythene partition. The left side is kept moist but the right side is kept dry. The radicals at first grow in downward direction due to the effect of gravity (positive geotropism) and light (Negative phototropism), but after some time, the roots bend toward the moist soil (Positive hydrotropism). This is evidently due to the affinity of germinating roots towards water.
Activity 7.3 | Page 123 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
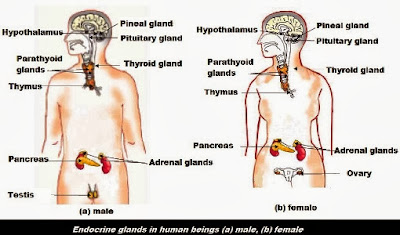
- Look at Fig.
Answer. The endocrine glands are :
| Hypothalamus | Pituitary Gland | Pineal gland | Thymus glands |
| Thyroid gland | Parathyoid glands | Adrenal glands | Pancreas |
| Testes | Ovaries |
- Some of these glands have been discussed in the text. Consult books in the library and discuss with your teachers to find out about the functions of other glands.
Intext Questions | Page 125 | Chapter 7. Control and Coordination| CBSE Class 10th Science
Question 1. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer. Chemical coordination takes place in animals through endocrine system which constitutes a second way of control and coordination in our body. Different endocrine glands, secret chemical substances called hormones to control and coordinate different body activities. It is important that hormones should be secreted in precise quantities. The timing and amount of hormone released are regulated by feedback mechanisms
Question 2. Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer. The use of iodised salt advisable because Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make thyroxin hormone. Thyroxin regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth. Iodine is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin. In case iodine is deficient in our diet, there is a possibility that we might suffer from goitre. One of the symptoms in this disease is a swollen neck.
Question 3. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Answer. When Adrenaline is secreted into the blood and carried to different parts of the body. The target organs such as heart, beats faster, resulting in increased supply of oxygen to our muscles which as a result, get surplus power to perform various activities against different demanding situations
Question 4. Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer.The patients of diabetes, who have inadequate levels of insulin produced by pancreas, are treated by giving injections of insulin. Insulin is a hormone which is produced by the pancreas and helps in regulating blood sugar levels. If it is not secreted in proper amounts, the sugar level in the blood rises causing many harmful effects.


No comments:
Post a Comment